How Essential Oils Work
Humans have interacted with plants for millennia and have discovered beneficial properties of plants. Essential oils are highly concentrated essences from plant material and a great way to harness Mother Nature’s gifts. Aromatherapy is the practice of using essential oils for their therapeutic benefits to humans. Each essential oil possesses unique properties and it is these properties that are most exciting when working with essential oils.
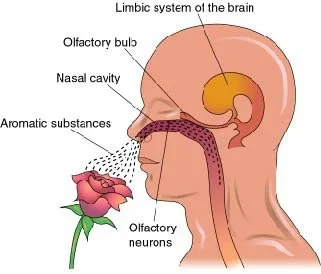
When inhaled, the scent molecules in essential oils travel from the olfactory nerves directly to the brain and especially impact the amygdala, the emotional centre of the brain.
During inhalation essential oil particles are quickly picked up by the cells in our nostrils and are absorbed via receptors into the mucous lining from where the scent reaches the ‘smell centre’ in the brain.
This ‘smell centre’ converts the inhaled aroma into a neural code which is relayed across to the limbic system (the body’s emotional centre) and further to the hippocampus followed by the hypothalamus. The information is then passed on to the pituitary gland and other endocrine glands to support hormonal balance.
The limbic system in the brain controls functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, memory, stress levels and hormone balance.
The molecules in the essential oils are small enough to allow them to penetrate through the skin.
When used topically, the oils can travel through the epidermis and reaching the dermis and to the blood vessels, this allows the essential oil molecules to circulate through to all body areas through the blood stream.
Most essential oils have antibacterial properties; some are antiviral, anti-fungal and/or anti-inflammatory. Essential oils also contain antioxidants which help to prevent cell damage and protect against the build up of toxic waste in skin cells.
The majority of essential oil constituents leave the body within hours, mainly through excretion via the kidneys, although their effects can last much longer within the tissues.